Batten siding, with its clean lines and versatile aesthetic, offers a captivating alternative to traditional siding options. This guide delves into the world of batten siding, exploring its diverse materials, installation techniques, design possibilities, and cost considerations. From understanding the advantages and disadvantages to mastering installation and maintenance, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about incorporating this striking siding choice into your next project. Whether you’re drawn to its rustic charm or its modern adaptability, this comprehensive overview will illuminate the multifaceted appeal of batten siding.
We’ll examine various materials, from the classic warmth of wood to the low-maintenance practicality of vinyl and fiber cement. We’ll explore different installation methods and design considerations, showcasing how batten siding can enhance a range of architectural styles, from charming farmhouses to sleek contemporary homes. Furthermore, we’ll provide a detailed cost analysis, helping you budget effectively for your project.
What is Batten Siding?
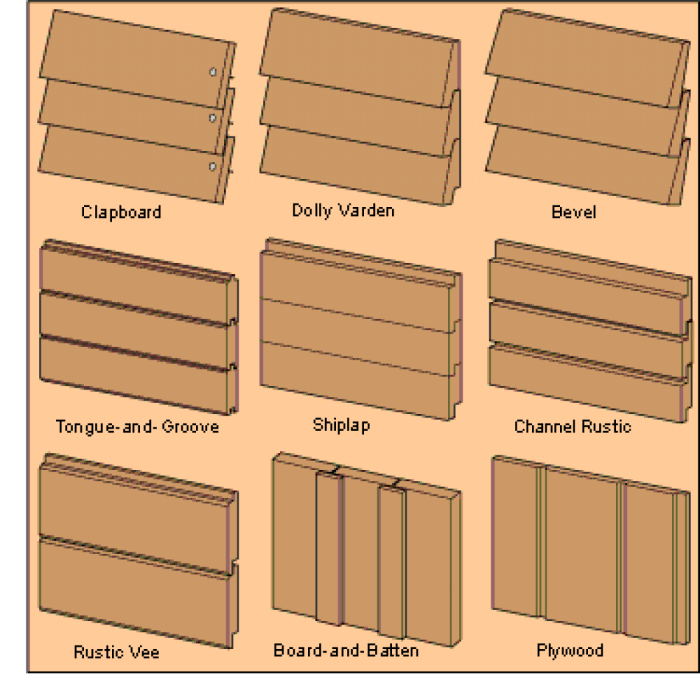
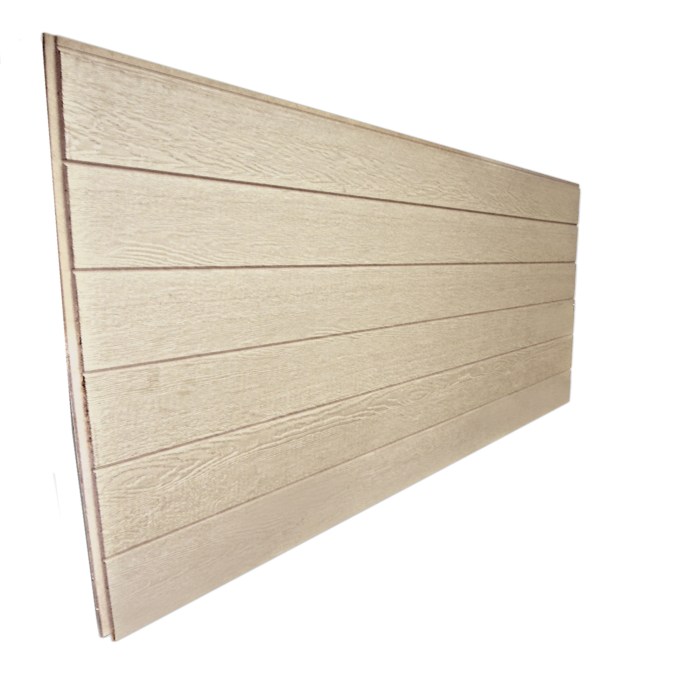
Batten siding, a classic and visually appealing exterior cladding option, features narrow, vertical boards installed directly onto the house’s framing or sheathing. Unlike traditional lap siding where boards overlap, batten siding boards are typically spaced apart, creating a visually striking and textured surface. This design allows for natural expansion and contraction of the material, minimizing the risk of warping or damage due to weather changes. The gaps between the battens can also improve ventilation, contributing to a healthier home envelope.
Batten siding offers a clean, modern aesthetic, easily adaptable to various architectural styles, from rustic farmhouses to contemporary homes. Its versatility stems from the wide array of materials and finishes available, allowing homeowners to achieve a personalized look that complements their property. The choice of material significantly impacts the siding’s durability, maintenance requirements, and overall cost.
Batten Siding Materials
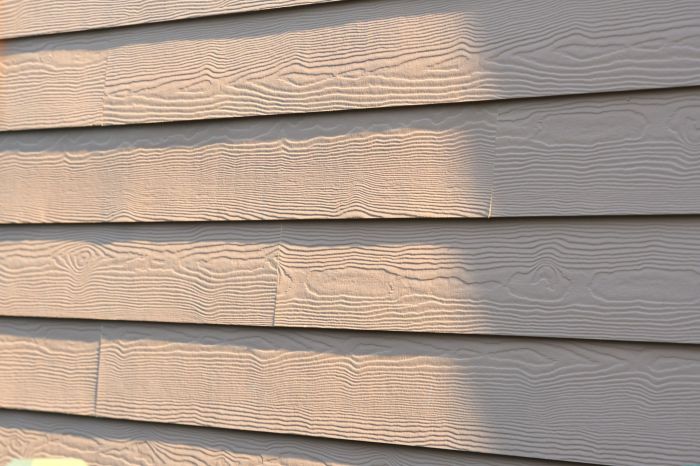
The selection of materials for batten siding directly impacts its longevity, maintenance needs, and aesthetic appeal. Common materials include wood, vinyl, and fiber cement, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages. Wood batten siding, for instance, provides a natural, warm look but requires regular maintenance to prevent rot, insect damage, and fading. Vinyl batten siding, on the other hand, is low-maintenance and resistant to moisture and insects, making it a popular choice for its durability and ease of care. Fiber cement batten siding combines the durability of cement with the aesthetic appeal of wood, offering a low-maintenance option that resists fire, rot, and insect infestation.
Batten Siding Installation
Installing batten siding involves several key steps, beginning with proper preparation of the wall surface. This includes ensuring the sheathing is sound and level, and installing any necessary weather barriers or moisture protection. The batten boards are then attached directly to the wall using appropriate fasteners, such as nails or screws. The spacing between the boards is crucial; a consistent gap is essential for proper ventilation and to prevent moisture buildup. This spacing is typically achieved using spacers or by precise measuring and marking during installation. Finally, caulk is applied to seal the gaps between the boards and the wall, preventing water intrusion and enhancing the overall weather resistance of the siding. Accurate measurements and careful installation are paramount to ensure a visually appealing and long-lasting result. Professional installation is often recommended, especially for larger projects or complex designs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Batten Siding
Batten siding, with its clean lines and versatile aesthetic, offers a unique approach to exterior cladding. However, like any building material, it presents both advantages and disadvantages that homeowners should carefully consider before making a decision. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making an informed choice that aligns with your budget, aesthetic preferences, and long-term maintenance goals.
Aesthetic Advantages of Batten Siding
The visual appeal of batten siding is a major selling point. Its simple, linear design lends itself to a variety of architectural styles, from rustic farmhouse to modern minimalist. The clean lines and vertical orientation can create a sense of height and elegance, enhancing the overall curb appeal of a home. The ability to customize the width and spacing of the battens allows for further personalization, creating a unique and visually striking exterior. Different paint or stain colors can also dramatically alter the look, making it adaptable to various design schemes.
Durability and Maintenance Aspects of Batten Siding
When properly installed and maintained, batten siding offers commendable durability. The material itself, typically wood or fiber cement, is inherently strong and resistant to weathering. However, the longevity is significantly influenced by the quality of the material and the application of protective coatings. Regular maintenance, such as repainting or restaining every few years, is essential to protect the siding from moisture damage, insect infestation, and UV degradation. This proactive approach ensures the siding retains its aesthetic appeal and structural integrity for an extended period.
Cost and Installation Complexity of Batten Siding
Batten siding generally falls into the mid-range to higher-end price bracket compared to other siding options like vinyl or aluminum. The cost is influenced by several factors, including material selection (wood type, fiber cement composition), labor costs for professional installation, and the complexity of the project. The installation process itself is more labor-intensive than simpler siding types due to the precision required in spacing and aligning the battens. This complexity often translates to higher overall installation costs.
Potential Issues with Batten Siding
While durable, batten siding is susceptible to certain issues if not properly installed or maintained. Water damage can occur if the battens aren’t properly sealed or if there are gaps in the installation. Wood batten siding is particularly vulnerable to insect infestation and rot if not treated with appropriate preservatives. Furthermore, the narrow profile of the battens can make repairs more challenging and potentially more expensive than with wider siding options.
Comparison of Batten Siding with Other Siding Types
Compared to clapboard siding, batten siding offers a more modern and streamlined aesthetic. Clapboard, with its overlapping horizontal design, has a more traditional look. Cost-wise, clapboard can be slightly less expensive, depending on the material. In terms of lifespan, both can last for decades with proper maintenance, although wood clapboard might require more frequent repainting. Shingle siding, with its textured and layered appearance, provides a distinct aesthetic from the clean lines of batten siding. Shingle siding can be more expensive than batten siding, especially if using natural materials like cedar or slate. Lifespan varies greatly depending on the shingle material, but generally, it can be comparable to batten siding.
Design Considerations for Batten Siding
Batten siding offers a remarkable degree of design flexibility, allowing for customization to suit diverse architectural styles and personal preferences. Careful consideration of pattern, material, and color choices can significantly impact the overall aesthetic and functionality of a structure. This section explores various design aspects to help you achieve the desired look and feel for your project.
Batten Siding Patterns and Designs
The arrangement of battens significantly influences the visual impact of the siding. Horizontal, vertical, and mixed orientations each create distinct styles. The spacing between battens also plays a crucial role, affecting the appearance of shadow lines and the overall texture. Wider gaps create a more rustic feel, while tighter spacing provides a cleaner, more modern look.
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
| Horizontal Batten Siding | This classic arrangement features horizontal battens, often spaced evenly, creating a clean and traditional look. It’s a popular choice for farmhouse and rustic styles, emphasizing the horizontal lines of the structure. Varying the batten width can add visual interest. For example, alternating wider and narrower battens can create a rhythmic pattern. |
| Vertical Batten Siding | Vertical battens offer a more contemporary feel, drawing the eye upward and creating a sense of height. This style works well with modern and minimalist designs. Consistent spacing between battens contributes to a clean, uncluttered look. The use of contrasting colors between battens and the underlying surface can add a bold accent. |
| Mixed Orientation Batten Siding | Combining horizontal and vertical battens can create a dynamic and visually engaging design. This approach allows for creative exploration, with possibilities including geometric patterns or the use of vertical battens as accents against a primarily horizontal background. This method works best when carefully planned to avoid a chaotic appearance. |
Batten Siding and Architectural Styles
Batten siding’s versatility allows it to complement a wide range of architectural styles.
Farmhouse Style: Horizontal batten siding in natural wood tones, often with wider gaps between battens, creates a classic farmhouse aesthetic. The use of weathered or reclaimed wood can enhance this rustic charm. Adding a contrasting trim color can further emphasize the traditional feel.
Modern Style: Clean lines and a minimalist approach are key to modern architecture. Vertical batten siding in a solid color, with consistent spacing and minimal ornamentation, works well. The use of materials like fiber cement or painted wood in neutral colors contributes to a sophisticated and contemporary look.
Rustic Style: Rustic designs often feature rough-hewn textures and natural materials. Horizontal batten siding with irregular spacing and variations in wood tones creates a sense of organic, handcrafted appeal. The use of reclaimed wood, with its natural imperfections, adds to the rustic charm. A natural wood stain or a weathered gray finish complements this style.
Batten Siding Layout for a Small Shed
This example details a batten siding layout for a 10ft x 8ft shed.
Material: Cedar wood battens, approximately 1 inch x 6 inches.
Color: A natural cedar stain, allowing the wood grain to show through.
Installation Details: Horizontal batten siding will be used. Battens will be spaced 1/2 inch apart. A waterproof underlayment will be installed before the battens. Each batten will be nailed securely to the underlying structure using galvanized nails. End caps will be added to the ends of each batten for a clean finish. The shed’s roofline will incorporate a contrasting dark brown trim.
Batten Siding Installation and Maintenance
Installing batten siding requires careful planning and execution to ensure a durable and aesthetically pleasing finish. Proper maintenance is equally crucial to prolong the lifespan of your siding and maintain its visual appeal. This section details the necessary steps for both installation and ongoing care.
Successful batten siding installation hinges on careful preparation and the use of appropriate tools and materials. Understanding the process and adhering to best practices will significantly impact the final result and the longevity of your siding.
Tools and Materials Required for Batten Siding Installation
Gathering the necessary tools and materials beforehand streamlines the installation process and minimizes interruptions. Having everything readily available ensures a smooth and efficient workflow.
- Measuring tape and level
- Circular saw or hand saw
- Drill with appropriate drill bits (for pilot holes and fasteners)
- Hammer or nail gun
- Safety glasses and gloves
- Exterior-grade wood siding (battens)
- Fasteners (galvanized nails or screws)
- Flashing (for windows and doors)
- Caulk
- Underlayment (e.g., housewrap)
- Strapping (for attaching siding to framing)
Step-by-Step Guide for Batten Siding Installation
The following steps provide a clear and concise guide to installing batten siding. Following this sequence will ensure a professional-looking and durable installation.
- Prepare the wall: Ensure the wall is clean, dry, and free of any debris. Install housewrap for added protection against moisture.
- Install strapping: Attach horizontal strapping to the wall framing, creating a level surface for the batten siding. Spacing should be consistent with the width of your batten boards, accounting for overlaps.
- Cut and measure battens: Accurately measure and cut the batten boards to the required lengths, allowing for overlaps and any necessary cuts around windows and doors.
- Install the first course: Begin at the bottom of the wall and install the first course of batten siding, ensuring it is level and aligned. Use galvanized nails or screws to secure the boards to the strapping, pre-drilling pilot holes to prevent splitting.
- Install subsequent courses: Continue installing subsequent courses, overlapping each board by a consistent amount (typically 1-2 inches). Maintain consistent spacing and alignment throughout the installation.
- Install flashing: Install flashing around windows and doors to prevent water penetration.
- Caulk gaps and seams: Apply exterior-grade caulk to seal any gaps or seams between the batten boards and around windows and doors.
Batten Siding Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is vital for preserving the beauty and longevity of batten siding. These procedures should be performed on a regular schedule to prevent damage and maintain the aesthetic appeal of the siding.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the siding using a soft brush, mild detergent, and water. Pressure washing should be avoided as it can damage the wood. For stubborn stains, use a wood cleaner specifically designed for exterior use.
- Painting: Depending on the type of wood and finish, repainting may be necessary every few years. Use an exterior-grade paint designed for wood siding to protect the wood from the elements and maintain its appearance. Proper surface preparation, including sanding and priming, is crucial for a long-lasting paint job.
- Repair: Address any damaged or rotting battens promptly. Replace damaged boards with new ones, ensuring a proper fit and secure fastening. Caulk any gaps or cracks to prevent water intrusion.
Cost and Budgeting for Batten Siding

Planning a batten siding project requires careful consideration of the associated costs. Understanding the various expense categories and factors influencing the final price is crucial for effective budgeting and avoiding financial surprises. This section provides a breakdown of typical costs and a sample budget to help guide your planning.
Material Costs
Material costs for batten siding installation represent a significant portion of the overall budget. These costs vary depending on several factors including the type of wood chosen (e.g., cedar, redwood, pine), the wood’s grade and quality, the dimensions of the battens, and the quantity needed. Additional materials like fasteners, flashing, and underlayment also contribute to the total material expense. Premium woods like cedar or redwood will naturally command higher prices than standard pine. The cost per board foot or linear foot will vary depending on your location and the supplier. Furthermore, consider the need for additional materials for trim work and any necessary repairs to the underlying structure before siding installation begins.
Labor Costs
Labor costs represent another significant portion of the overall project expense. The hourly rate for skilled labor varies geographically and is influenced by factors such as experience, demand, and the complexity of the installation. The total labor cost is directly proportional to the size of the project and the complexity of the installation. A larger surface area requires more time, thus a higher labor cost. Similarly, intricate designs or difficult-to-access areas increase labor hours and therefore the overall cost. Consider that specialized skills might be needed for complex installations or unique design features.
Permit Costs
Building permits are typically required for exterior home renovations, including batten siding installation. Permit fees vary depending on your local jurisdiction and the scope of the project. Contact your local building department for specific cost estimates and required documentation. Factors such as the size of your home and the extent of the work (e.g., whether it involves structural changes) can influence the permit cost. It is essential to factor permit fees into your budget from the outset to avoid unexpected delays or penalties.
Factors Influencing Overall Cost
Several factors beyond material, labor, and permits can impact the overall cost of batten siding installation. These include:
- Home size and complexity: Larger homes or those with complex architectural features require more materials and labor, leading to higher costs.
- Existing siding removal: If you are replacing existing siding, the cost of removal and disposal adds to the overall expense.
- Site accessibility: Difficult-to-access areas or challenging terrain can increase labor costs.
- Region and market conditions: Material and labor costs vary geographically and are subject to market fluctuations.
- Finishing and detailing: Custom detailing, intricate trim work, or specialized finishes can significantly increase the overall cost.
Sample Budget for a 1000 sq ft House
The following table presents a sample budget for a batten siding project on a 1000 sq ft house. Note that these figures are estimates and can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above.
| Item | Quantity | Unit Cost | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batten Siding (Cedar) | 1500 sq ft | $8/sq ft | $12000 |
| Fasteners and Flashing | 1 set | $500 | $500 |
| Underlayment | 1000 sq ft | $2/sq ft | $2000 |
| Labor (Installation) | 100 hours | $50/hour | $5000 |
| Permits | 1 | $500 | $500 |
| Total Estimated Cost | $20000 |
Visual Representation of Batten Siding

Batten siding, with its clean lines and versatile aesthetic, offers a wide range of visual possibilities for homeowners seeking to enhance their property’s curb appeal. The choice of material, color, and pattern significantly impacts the overall look, creating a unique and personalized exterior. Understanding these visual aspects is crucial for making informed decisions during the design and construction phases.
The appearance of batten siding varies greatly depending on the chosen material. Wood batten siding, for instance, offers a natural, rustic charm. The texture can range from smooth, planed surfaces to more rugged, textured finishes, depending on the type of wood and the level of processing. Color options are virtually limitless, from warm honey tones and rich browns to weathered grays and deep, almost black stains. The natural grain of the wood is often visible, adding depth and character. In contrast, vinyl batten siding provides a more uniform, smooth surface with less textural variation. While it lacks the natural grain of wood, it offers a wide array of colors, including those mimicking the appearance of wood, and requires less maintenance. Fiber cement batten siding presents a different visual profile altogether. It offers a more durable, low-maintenance option with a subtle texture that can be painted in a wide array of colors to achieve a variety of aesthetic effects. The painted finish tends to be more uniform than wood, allowing for bolder color choices.
Material and Color Influences on Batten Siding Appearance
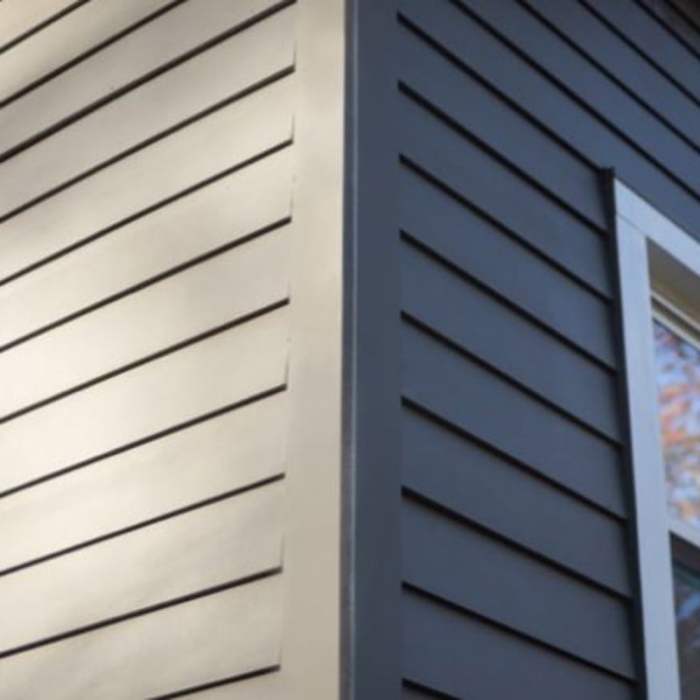
The interplay of material and color significantly shapes the overall visual impact. Imagine a home clad in wide, dark brown cedar batten siding. The deep color creates a sense of richness and sophistication, while the natural wood grain adds visual warmth. The same home, clad in narrow, white vinyl batten siding, would project a completely different feel – clean, modern, and perhaps even minimalist. A home featuring fiber cement batten siding painted a vibrant teal would offer a fresh, contemporary look, while a home with gray fiber cement siding would exude a more subdued elegance. The texture also plays a role; a rough-hewn wood siding offers a rustic feel, while smooth vinyl or fiber cement provides a sleek, contemporary look.
Visual Impact of Different Batten Siding Patterns and Widths
The width of the battens and the pattern in which they are arranged significantly influence the overall appearance. Wide battens create a bold, modern statement, while narrower battens provide a more refined, traditional look. Consider a house with wide, vertically oriented batten siding; the vertical lines draw the eye upward, making the house appear taller and more imposing. In contrast, horizontally oriented batten siding, especially with narrower battens, can create a sense of spaciousness and calmness. A staggered pattern, where the battens are offset, adds visual interest and texture, while a more uniform, aligned pattern offers a cleaner, more contemporary feel. Imagine a craftsman-style home with a mix of wide and narrow battens, arranged in a staggered pattern; this creates a rich, visually engaging facade. Conversely, a sleek modern home might feature uniformly sized, horizontally aligned battens for a streamlined aesthetic.
Lighting Effects on Batten Siding Appearance
The way light interacts with batten siding significantly impacts its appearance throughout the day. During the morning, the low-angled sunlight can highlight the texture of the siding, accentuating the grain of wood or the subtle texture of fiber cement. The colors appear richer and more vibrant. As the sun moves higher in the sky, the light becomes more even, softening the shadows and creating a more uniform appearance. In the evening, artificial lighting can dramatically alter the perception of color and texture. Warm, incandescent lighting can make the siding appear more inviting and cozy, while cooler, LED lighting might create a more modern and sleek feel. The interplay of light and shadow throughout the day constantly transforms the visual experience of the batten siding, adding depth and dynamism to the home’s exterior.
Ultimately, the decision to use batten siding hinges on a careful assessment of your project’s specific needs and aesthetic goals. Weighing the advantages of its unique visual appeal and potential durability against the considerations of cost and installation complexity is crucial. By understanding the nuances of material selection, design choices, and maintenance requirements, you can confidently incorporate batten siding to achieve a stunning and enduring exterior for your home or building. This guide provides a solid foundation for making informed choices, empowering you to transform your vision into reality.
FAQs: Batten Siding
What is the lifespan of batten siding?
The lifespan of batten siding varies significantly depending on the material. Wood siding, with proper maintenance, can last 20-50 years. Vinyl and fiber cement options generally offer longer lifespans, often exceeding 30-50 years.
Can I install batten siding myself?
While DIY installation is possible, particularly for smaller projects, it requires specific skills and tools. For larger projects or complex designs, professional installation is often recommended to ensure proper results and longevity.
How often should I paint batten siding?
The frequency of repainting depends on the material and environmental factors. Wood siding may require repainting every 3-5 years, while properly primed and painted fiber cement can last much longer.
What are the best cleaning methods for batten siding?
Regular cleaning with a soft brush and water is usually sufficient. For stubborn stains, a mild detergent solution can be used. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the siding’s finish.
Is batten siding suitable for all climates?
While batten siding is relatively durable, certain materials are better suited for specific climates. For example, wood siding may require more maintenance in humid or wet environments, while fiber cement offers superior resistance to moisture.



